Mouth ulcers
Almost everyone has ulcers in the mouth from time to time. The lining of the mouth may be damaged by jagged teeth, very hot food or drink, or strong antiseptics or mouthwashes. These ulcers usually heal quickly without treatment. Other mouth ulcers are usually caused by infections.
Some ulcerative mouth affections are described below:
Traumatic ulceration
Traumatic causes of oral ulceration may be physical or chemical. Physical damage to the oral mucosa may be caused by sharp surfaces within the mouth, such as components of dentures, orthodontic appliances, dental restorations, or prominent tooth cups.
Erosive lichen planus
Lichen planus is one of the more prevalent Mucocutaneous disorders. The cause of lichen planus is not known, although it is immunologically mediated and resembles in many ways a hypersensitive reaction to an unknown antigen. T-lymphocyte-mediated destruction of basal keratinocytes and hyperkeratinization produces the characteristic clinical lesions. Lichen planus characteristically presents as white patches or striae that may affect any oral site.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis refers to any inflammatory reaction affecting the oral mucosa, with or without ulceration that may be caused or intensified by local factors.
Normal oral pigmentation
Melanin is a normal skin and oral pigment produced by melanocytes. Increased melanin deposition in the oral mucosa may occur in various diseases. The pigmentation is more prominent in areas of pressure or friction and becomes more intense with aging.
Leucoedema – leucoedema is a normal anatomical variant of the oral mucosa due to increased thickness of the epithelium and intracellular edema of the malpeghian layer. Clinically, the mucosa has a grayish white color with slight wrinkling, which disappears if the mucosa is distended by pulling or stretching of the cheek.
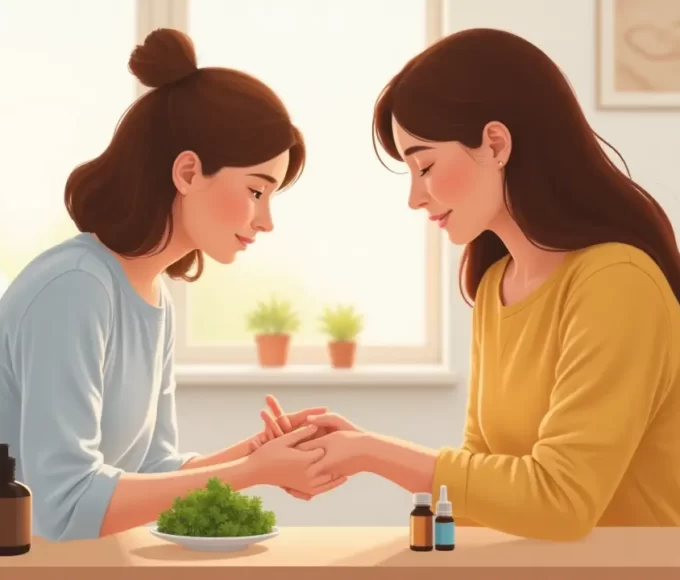
Homeopathic treatment of diseases of mouth
Homeopathy is one of the most popular holistic systems of medicine. The selection of remedy is based upon the theory of individualization and symptoms similarity by using holistic approach. This is the only way through which a state of complete health can be regained by removing all the sign and symptoms from which the patient is suffering. The aim of homeopathy is not only to treat diseases of mouth but to address its underlying cause and individual susceptibility. As far as therapeutic medication is concerned, several remedies are available to treat diseases of mouth that can be selected on the basis of cause, sensations and modalities of the complaints. For individualized remedy selection and treatment, the patient should consult a qualified homeopathic doctor in person. There are following remedies which are helpful in the treatment of diseases of mouth:
Merc Sol.
pain due to the inflamed gums or the membrane of the socket; worse at night and in damp weather; teeth feel elongated and sore, soreness becoming worse from warmth and affecting the whole jaw; painful ulceration at the root of the teeth; gums swollen, ulcerated and retracted, with offensive odor from the mouth.
Silicea
Abscesses in roots of the teeth, or dental fistulae, pains are worse from eating warm food, or when cold air gets into the mouth; worse at night; teeth feel loose.
Plantago
teeth feel elongated, sore and sensitive to touch; cheeks swollen; pains are periodic, easily excited and affect the sound teeth; worse lying on affected side; sometimes stabbing and boring pains become severe.
Staphysagria
The gums are unhealthy and are retracted. the teeth have a tendency to decay an turn black; gnawing sensation in the roots of the decayed teeth.
Arnica
Useful after extraction of tooth.
Coffea
It removes the severest pains due to cold; the pain is often relieved by cold iced water. it is the best remedy for stinging, jerking pains.
Chamomilla
For persons who drink much coffee; for pains in decayed teeth after taking cold during perspiration, or if the decayed tooth is too long and loose.
Belladonna
for pains which cause restlessness, the patient running about with the disposition to cry; when pain radiates from one tooth in all directions; worse during the night or after going to bed, in the open air, after meal and when touched, or biting, when hot liquids come in contact; and the throat is dry with great thirst.
Arsenicum
when the teeth seem loose and elongated with jerking and throbbing pains, worse when touched, when lying on the affected side, and when at rest, and also from cold, better by heat of the stove, by hot applications, by sitting up in bed; it is suitable when pains are very weakening, or when the patient feels feverish, and when the finger tips are cold.
Borax
Aphthous inflammation of the mouth which is very hot and dry; mucus membrane bleeds easily; child starts up in fright, throws his arms about, is pale and livid and looks shriveled up; offensive breath; puffy, indebted tongue. Also indicated in thrush when located on the inner surface of the cheek; may be also on tongue and fauces.
Helleborus nig
Aphthae with increased saliva. cankers with yellowish- red edges.
Hydrastis
One of the best remedies for aphthous stomatitis in poorly nourished children; the membrane is full of ulcers and the tongue is coloured yellow, or is large and flabby with imprints of teeth; excessive secretion of thick tenacious mucus.
salicylic acid
Common, painful and depressed sores.
Baptisia
Indicated in parasitic stomatitis or thrush; condition in which blood oozes from the gums, which is dark red and offensive; great foetid salivation; gums ulcerated, tongue is cracked and mouth is exceedingly offensive; mucus membrane is in a most unhealthy condition.
Mercurius
This is also indicated in thrush; sore mouth with salivation; tendency to ulceration of all forms, especially flat and superficial ulcers; the presence of diarrhoea is an essential indication; gums are spongy and swollen; the glands about the neck are also swollen.
Lachesis
Blisters on the inflamed tongue, which change into ulcers.
Sulphuric Acid-
Mouth and tongue covered with blisters and ulcers; breath offensive and gums are white.
Apis
Acute oedema; tongue fiery red, swollen, sore, and raw with vesicles; tongue trembling, gums swollen.
Muriatic Acid
Tongue pale, swollen, dry, leathery, paralyzed; deep bluish or hard lumpy ulcers on tongue; foetid breath