An impacted fracture is a type of bone fracture that occurs when the broken ends of a bone are driven into each other. This compression of bone fragments can cause severe pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Understanding the basics of an impacted fracture, including its definition, anatomy, and types, is essential for recognizing the condition and seeking the proper treatment.
In children, an impacted fracture is often referred to as a buckle fracture, a milder but still painful injury where the bone bends or compresses rather than breaking completely. Whether the fracture is the result of a fall, a car accident, or a high-impact sports injury, timely diagnosis and treatment are key to ensuring a full and proper recovery.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about impacted and buckle fractures, including what they are, how they are diagnosed, how they are treated, and what to expect during recovery, all explained in clear, easy-to-understand language, grounded in medical accuracy and real-world empathy.
What Is an Impacted Fracture?
In simple terms, an impacted fracture occurs when two pieces of a broken bone are jammed together under force. This results in the bone compressing instead of separating. A helpful visual might be crushing a soda can: the aluminum collapses inward but remains in one piece. This type of fracture is prevalent in long bones, such as the femur, tibia, or radius, where sudden pressure from a fall or accident forces one fragment to displace another.
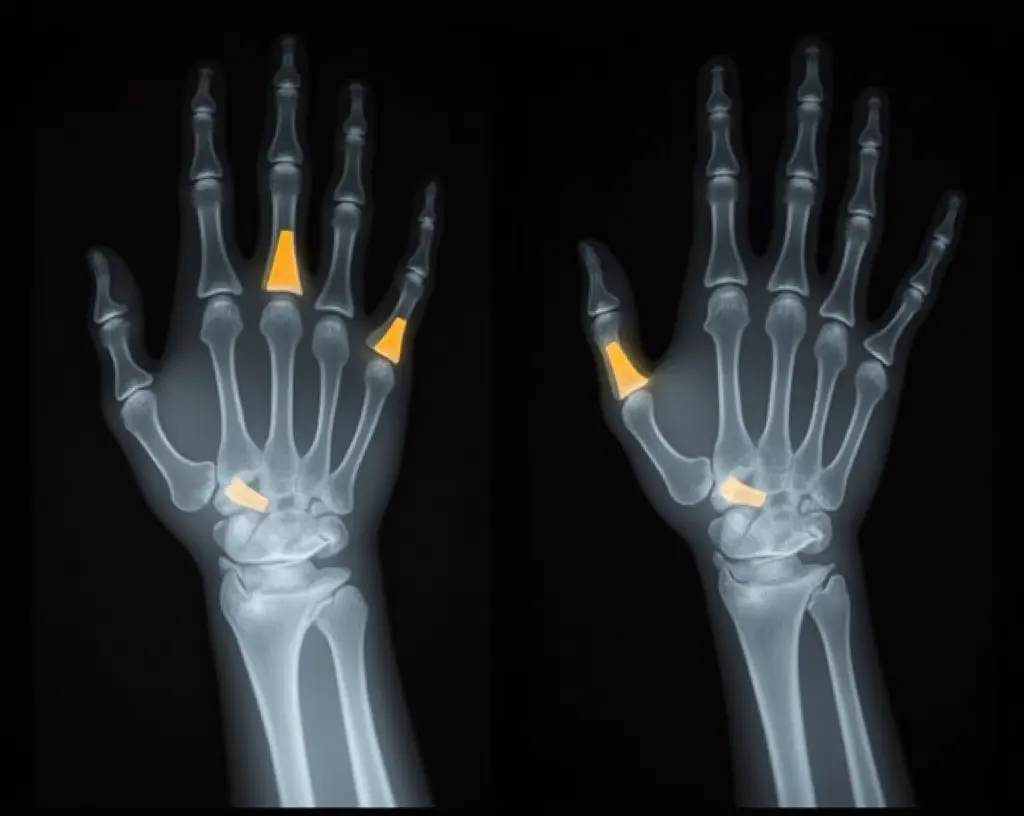
In children, impacted fractures are commonly referred to as buckle fractures. These are incomplete fractures that typically occur in soft, pliable bones. Because children’s bones are still developing, they’re more likely to bend or compress rather than snap, making buckle fractures one of the most common bone injuries in kids under 12.
Types of Impacted Fractures
Buckle Fracture can vary based on the direction of the force and how the bone fragments align after injury. The two most recognized types include:
Valgus Impacted Fracture
This occurs when the distal (lower) part of the fractured bone is angled outward, away from the body’s midline. It’s most commonly seen in hip and femoral neck fractures. The force pushes the bone sideways, often resulting in joint misalignment that can affect stability.
Varus Impacted Fracture
In a varus-impacted fracture, the distal fragment is pushed inward toward the midline of the body. This angulation creates pressure on the inner part of the joint and may affect the bone’s ability to bear weight evenly, especially in the hip or leg bones.
Both types require careful diagnosis, as their orientation affects treatment plans, particularly when surgical intervention is necessary. The distinction between valgus and varus angulation is vital for orthopedic surgeons to determine the proper approach to realignment and fixation.
How Do Impacted Fractures Happen?
Impacted fractures usually result from trauma events where force travels directly through a bone, pushing the ends into each other. This can happen during car accidents, sports collisions, or falls from a significant height. Even a seemingly minor fall can cause a fractured bone in individuals with weakened bones, especially older adults with osteoporosis.
For children, it often occurs when they land on an outstretched arm during a fall, compressing the bones in the forearm. In older adults, the hip and spine are most vulnerable, particularly because of natural age-related bone thinning.
Symptoms of an Impacted Fracture
Recognizing the symptoms of an impacted fracture early can make a significant difference in how quickly and effectively the injury is treated. While symptoms may vary depending on the affected bone and the severity of the fracture, several common signs tend to appear in most cases.
Pain is often immediate and localized at the site of the injury. It tends to worsen with movement or pressure. Swelling and bruising usually appear within hours, frequently accompanied by tenderness or a noticeable bulge. In more severe cases, the limb may look misshapen or show an unnatural curve, especially when the bone ends are forcefully compressed.
In pediatric patients, symptoms may be more subtle. For example, a child with a buckle fractured wrist may not be able to describe their pain clearly but might avoid using the injured hand or cry when the wrist is touched. They may also favour the uninjured arm, refuse to pick up toys, or stop engaging in everyday activities altogether.
Because buckle fractures of the wrist are a typical result of falls in children, particularly those under 12, parents should pay close attention to even minor complaints after a fall involving the arms. Prompt recognition of these signs and seeking a medical evaluation can prevent complications and lead to a faster recovery.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a Buckle Fracture begins with a thorough physical examination and a clear understanding of how the injury occurred. A healthcare provider will review the patient’s symptoms, check for visible deformities, and assess the function and range of motion of the affected area. Swelling, tenderness, bruising, or an inability to move the limb are all signs that raise suspicion of a fracture.
However, a physical exam alone is often not enough. To confirm the presence and type of fracture, especially in cases involving subtle or incomplete breaks, imaging tests are essential.
X-rays are the first and most commonly used diagnostic tool. They offer a detailed view of the bone structure and can show whether the fractured ends have been driven into each other, a hallmark of an impacted fracture. In children, buckle fractures can also be identified on an X-ray, typically presenting as a bulge or buckling of the bone’s surface without a complete break. These are especially common in the distal radius following a fall onto an outstretched hand.
In more complex or unclear cases, healthcare providers may order a CT scan to assess the depth, alignment, and involvement of surrounding joints. For injuries suspected to involve soft tissue damage, such as ligaments, tendons, or muscles, an MRI may be necessary. These advanced imaging techniques help determine whether the fracture is stable and whether surgical intervention might be required.
Early and accurate diagnosis is critical, particularly for buckle fractures and impacted fractures, as both often present with minimal deformity but require precise treatment to ensure proper healing and avoid complications.
Treatment for Impacted Fractures
The treatment plan for an impacted fracture depends on several key factors, including the location and severity of the break, whether the bone fragments are correctly aligned, and the patient’s age and overall health. In many cases, particularly with stable fractures, non-surgical treatment is sufficient.
For children and patients with mild or incomplete impacted fractures, immobilization using a splint or cast is often enough. This keeps the bone in place and allows it to heal naturally. Pain is managed with over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, and most children fully recover in just a few weeks.
In more severe cases, particularly when bone fragments are misaligned or the fracture is near a joint, doctors may perform a closed reduction to reposition the bones manually. This is typically done under anaesthesia and followed by immobilization.
If the fracture is complex or unstable, surgical intervention may be required. A procedure known as open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is used to align the bone and secure it using metal plates, screws, or rods. After surgery, physical therapy is often necessary to restore strength and mobility.
Throughout the healing process, patients are advised to attend regular follow-up appointments to ensure optimal recovery. These help monitor bone recovery and ensure that no complications such as malunion (improper healing), nonunion (failure to heal), or chronic stiffness develop.
Recovery and Healing Time
The recovery timeline for a fractured bone varies depending on several factors, including the affected bone, the severity of the compression, the patient’s age, and the chosen treatment method. Generally, impacted fractures have a more stable configuration compared to displaced fractures, which often allows for faster healing.
In children with buckle fractures, recovery is typically rapid. Most kids can return to normal activities within 2 to 4 weeks. Because their bones are still growing and highly regenerative, long-term effects are rare when properly managed.
In adults, especially those with fractures in weight-bearing bones, such as the femur or hip, the healing process can take longer, typically 6 to 12 weeks or more. Patients who undergo surgery may also require an extended rehabilitation period, including physical therapy, to rebuild muscle strength, restore range of motion, and support a full recovery of function.
Regardless of age or severity, following the prescribed treatment plan, attending follow-up visits, and adhering to physical therapy are key to ensuring a smooth and complete recovery.
Potential Complications of an Impacted Fracture
While most Buckle fractures heal without serious complications, delays in diagnosis or inadequate treatment can lead to long-term issues.
Malunion is a condition in which the bone heals in an incorrect position. This can result in deformity, reduced mobility, or chronic pain. Nonunion, though less common in impacted fractures, occurs when the bone fails to heal completely. It may require additional intervention, such as bone grafting or revision surgery.
Fractures near joints also increase the risk of joint stiffness, reduced range of motion, or post-traumatic arthritis. In rare cases, nerves or blood vessels near the fracture site can be damaged, leading to numbness, tingling, or impaired circulation.
Early diagnosis, proper imaging, and adherence to the recommended treatment plan significantly reduce these risks.
How to Prevent Impacted Fractures
Though accidents can’t always be avoided, there are practical steps you can take to reduce the risk of sustaining an impacted fracture.
For children, supervision during active play and the use of appropriate protective gear in sports can prevent falls and injuries. Creating safe play environments and teaching children how to fall safely, such as avoiding the direct extension of their arms, can also help.
In adults, particularly seniors, fall prevention is crucial. This includes making home environments safer by removing tripping hazards, installing grab bars in bathrooms, improving lighting, and avoiding slippery footwear.
A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, along with weight-bearing exercises, can strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures. Individuals over 50 or those with a family history of osteoporosis should discuss regular bone density tests and early intervention options with their doctor.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you suspect a Buckle Fracture, whether in yourself or a loved one, it’s essential not to delay medical evaluation. Even if the pain is tolerable, the injury may still be severe and could worsen without proper treatment.
You should visit the emergency room or urgent care center immediately if:
There is intense pain or swelling that worsens with time
- The limb appears deformed, misaligned or has an unusual bump
- You observe bruising or discoloration soon after trauma
- There is an inability to move or bear weight on the affected area
- A child suddenly avoids using a limb or displays visible discomfort during an activity
- You can visibly see the bone pushing through the skin (open fracture)
- There are numbness, tingling, or signs of poor blood flow
Prompt evaluation and early intervention not only ensure proper healing but also help avoid complications that can extend the recovery timeline.
Conclusion
Impacted fractures, though painful and often alarming at first, are highly treatable with the proper care and attention. Whether it’s a child recovering from a buckle fracture or an adult managing a compression injury after a fall, adequate diagnosis, guided treatment, and structured rehabilitation lead to excellent outcomes in most cases.
Recognizing the symptoms, seeking early medical care, and understanding your treatment options are essential. Don’t try to “tough it out” or self-diagnose. Bones need structure and time to heal correctly, and ignoring the signs of an impacted fracture can lead to preventable complications.
If you or someone you care for may have suffered a fractured bone that is not visible on X-ray, consult a qualified healthcare provider immediately. Early care leads to faster healing, less pain, and a stronger, safer recovery.
So, what’s the bottom line? While any fracture sounds scary, from my clinical experience, I can tell you that the outlook for a buckle fracture is excellent. It’s a sign that a child’s bones did what they were supposed to do—bend instead of breaking completely. The most important thing you can do is get it checked out. A little bit of care in the beginning ensures a strong, healthy, and speedy recovery for your child.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How serious is a buckle fracture?
A buckle fracture is generally considered a mild and stable type of fracture, especially common in children. Although it’s not as severe as a complete break, it still requires medical evaluation and proper care to ensure correct healing.
Will a buckle fracture need a cast?
Not always. Most buckle fractures are treated with a removable splint or soft cast, especially in children. The goal is to immobilize the bone while it heals, but full hard casts are usually not necessary unless the fracture is more severe.
How long does it take to recover from a buckle fracture?
Recovery typically takes 2 to 4 weeks in children. The healing process may be slightly longer in adults, depending on bone density and overall health. Most patients return to regular activity shortly after the splint is removed.
What is the difference between a buckle fracture and a regular fracture?
A buckle fracture is an incomplete fracture where the bone compresses and bulges but doesn’t break all the way through. A regular fracture usually refers to a complete break or crack that separates the bone into two or more pieces.
How do they fix a buckle fracture?
Buckle fractures are typically treated with immobilization, such as a wrist splint or soft cast. Surgery is not needed. The bone heals naturally over time, and pain is managed with over-the-counter medications.
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Muhammad Usman
References
- Nemours KidsHealth. Buckle Fractures – Overview of what buckle fractures are and how they occur in children due to bone compression. KidsHealth
- Pediatric Torus (Buckle) Fracture – StatPearls (NCBI Bookshelf) – Highlights that buckle fractures are common and managed non-surgically. NCBI
- Royal Children’s Hospital (Australia). Fracture Care: Buckle Injury – Describes splinting care and typical recovery for pediatric buckle fractures. Royal Children’s Hospital
- Medical News Today. Buckle Fractures: Causes, Recovery, and More – Details symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and recovery times. Medical News Today
- Healthline. Buckle Fracture: Causes, Recovery, and More – Discusses the nature of buckle fractures (torus fractures), especially in children. Healthline
- Verywell Health. Buckle Fracture: Treatment and Recovery – Explains treatment options (splint vs cast) and healing expectations. Verywell Health
- Wikipedia. Torus Fracture (Buckle Fracture) – Offers medical definitions, mechanism of injury, and prevalence in pediatric populations. Wikipedia
- Access Ortho. Greenstick and Buckle Fractures – Explains the mechanism of injury and common locations in children. Access Ortho
- Premier Health. Buckle Fracture: A Common Childhood Hazard – Covers diagnostic methods and treatment using splints/casting practices. Premier Health
- Cleveland Clinic. Bone Fractures: Types, Symptoms & Treatment – Provides a broader context on fracture classifications and treatment modalities. Cleveland Clinic





Leave a comment